Introduction
There exists an academic conflict relating to the authorship of the quote, “First they ignore you, then they laugh at you, then they fight you, then you win,” frequently credited to Mahatma Gandhi. However, the adoption of this aphorism by supporters of Bitcoin is unassailable.
Proponents of Bitcoin regularly anticipate the capacity of Bitcoin to supplant the United States dollar as the dominant international shop of worth. A less regularly attended to yet important query issues the mechanics of such a shift, consisting of the possible threats that might emerge, especially in the occasion that providers of fiat currency participate in active resistance versus difficulties to their financial monopolies.
Critical concerns emerge: Will the United States federal government and other Western countries adjust to the development of a Bitcoin requirement, or will they execute limiting steps to prevent the displacement of fiat currencies? Furthermore, should Bitcoin ascend beyond the dollar as the preeminent legal tender, will this shift be smooth and positive—comparable to the shift from Blockbuster Video to Netflix—or will it stimulate circumstances similar to Weimar Germany and the Great Depression? Alternatively, could it manifest as a compromise in between these extremes?
These questions go beyond theoretical interest; they hold considerable ramifications for the Bitscoins.netmunity. Should Bitcoin hold up against the possible turmoil ahead, it will be crucial for its supporters to think about how to strengthen Bitcoin versus these future circumstances and plan for the most serene and minimally disruptive shift to an economy anchored once again in sound cash concepts.
Particular attention needs to be paid to the vulnerabilities dealt with by people within lower-income brackets—those who, due to present and future Bitcoin assessments, might have a hard time to conserve properly in the middle of upcoming financial difficulties. The dismissive retort, “Have fun staying poor,” typically echoed by Bitcoin supporters towards doubters, threats ignoring the intensity of genuine recession circumstances. The implications of stopped working fiat financial policies will disproportionately affect those reliant on federal government expense for their financial stability. In democratic contexts, populist motions throughout the political spectrum might exploit this discontent, cultivating bitterness amongst the non-Bitcoin-owning bulk versus the elite who have Bitcoin possessions.
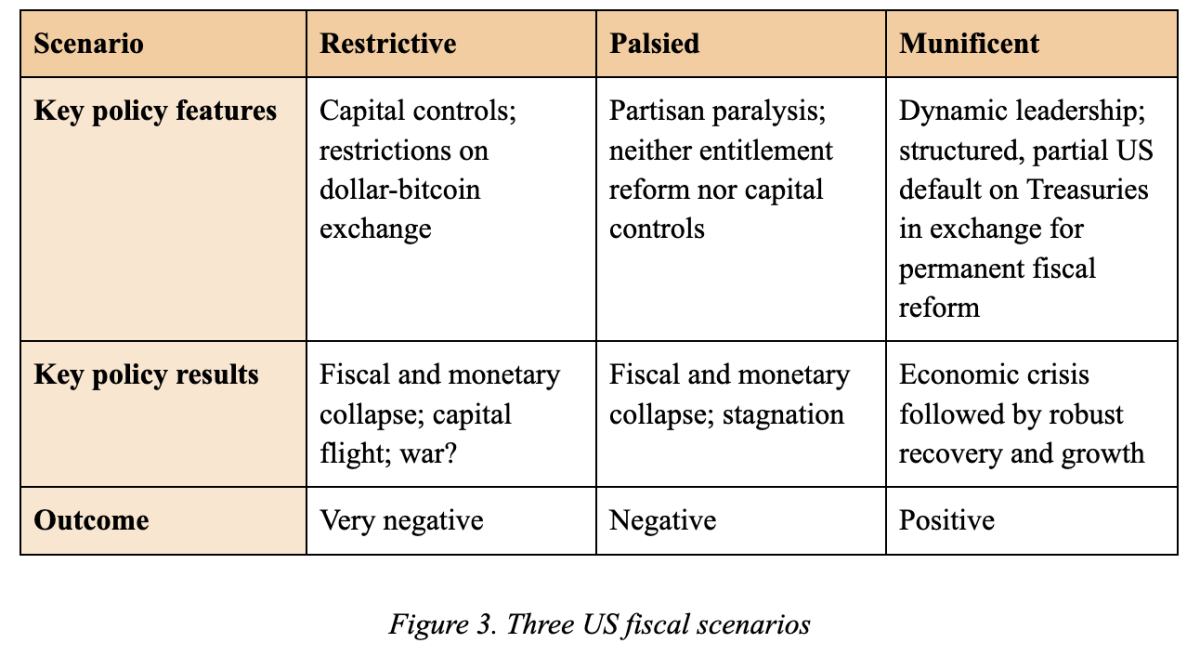
While anticipating the exact action of the United States federal government to a potential financial and financial collapse years for this reason is naturally difficult, it is possible to classify possible actions into typically unfavorable, neutral, or favorable results for society as a whole. This essay marks 3 such circumstances: a limiting situation, where the United States enacts rigid steps to reduce financial liberties to alleviate competitors with Bitcoin; a palsied situation, in which partisan and ideological rifts block efficient governance, preventing any advance towards financial enhancement or Bitcoin guideline; and a munificent situation, in which the United States incorporates Bitcoin into its financial structure while restoring sound financial policy. These circumstances are notified by the most likely development of a financial and financial crisis in the United States by 2044.
This analysis mainly focuses on the United States context, as the dollar presently works as the world’s reserve currency, making the United States federal government’s action to Bitcoin especially substantial.
The Coming Fiscal and Monetary Crisis
Current trajectories recommend that a substantial financial crisis in the United States is not simply possible however likely by 2044 unless there is a restorative modification in policy. Notably, in 2024, interest payments on federal financial obligation went beyond expenses on nationwide defense for the very first time in contemporary history. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO), the main nonpartisan financial arbiter for the nationwide legislature, cautions that federal financial obligation held by the public might reach around $84 trillion by 2044, relating to 139 percent of gdp, up from $28 trillion or 99 percent of GDP in 2024.
The CBO’s projections rest on numerous positive presumptions about the financial landscape in 2044, consisting of a robust yearly financial development rate of 3.6% in all time, the capability of the United States federal government to obtain at beneficial rates, and the lack of legal actions that would worsen financial difficulties.
In May 2024, the CBO acknowledged the positive nature of its forecasts, offering analyses of alternative financial circumstances that would affect the debt-to-GDP ratio. One situation, identified by rate of interest boosts of 0.05% greater yearly than the standard, would raise 2044 financial obligation to $93 trillion or 156% of GDP. Another option, in which federal earnings and costs stay constant with historic averages, tasks for 2044 a financial obligation of $118 trillion or 203% of GDP.
Nonetheless, an assessment of combined elements reveals a possibly alarming future. For circumstances, if the CBO’s increased rate of interest situation is paired with a steady GDP development decrease to 2.8%, the 2044 financial obligation forecast might intensify drastically to $156 trillion or 288% of GDP. By 2054, this figure might reach an astonishing $441 trillion or 635% of GDP.
View the initial post to see ingrained media.
Figure 1. United States debt-to-GDP ratio: Alternative circumstances
Credit: Avik Roy, https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/18398503/.
In a circumstance identified by raised interest payments and depressed financial development, the United States federal government would deal with an interest commitment of $6.9 trillion by 2044, taking in almost half of all federal tax earnings. Just as forecasts about continual financial development cannot be considered given, expectations for steady need for United States federal government financial obligation are similarly unpredictable. The need of lacking resources will ultimately emerge. Credit Suisse approximates that international home wealth totaled up to $454 trillion in 2022, consisting of the net worth of financial and property possessions, omitting financial obligations. The part of that wealth offered for providing to the United States federal government is lessening, as evidenced by the decreasing share of Treasury securities held by foreign and global financiers given that the 2008 financial crisis. Concurrently, while the need for Treasuries reduces, the supply of such securities continues to increase.
View the initial post to see ingrained media.
Figure 2. Ownership of United States Treasuries
Credit: Avik Roy, https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/7641395/.
Such disparities in the bond market would usually set off a decrease in bond rates, suggesting greater rate of interest. The Federal Reserve, nevertheless, has actually stepped in to keep lower rate of interest, deciding to buy Treasury securities through recently printed United States dollars to neutralize an absence of market self-confidence. This technique suggests a choice for financial inflation over allowing increasing rate of interest that would show lessened credit reliability.
This situation is unsustainable. Economist Paul Winfree, using an approach stemmed from International Monetary Fund research study, tasks that the federal government will tire its financial capability for accommodating extra financial obligation in the next 15 years—by 2039. Winfree highlights that rate of interest and possible GDP development will substantially affect these forecasts.
For the function of this analysis, it is presumed that the United States will experience a financial and financial collapse by 2044—a recession identified by intensifying rate of interest driven by inadequate market interest in Treasuries and intense customer rate inflation sustained by quick financial growth. During this two-decade duration, Bitcoin’s worth may rise to a level where its overall market capitalization attains competitiveness with that of United States Treasuries. A circumstance of competitive liquidity is essential, as it recommends that big institutional stars, such as federal governments and international banks, might obtain Bitcoin in significant volumes without causing considerable rate interruption. Based on common habits in financial markets, Bitcoin’s market capitalization is approximated to reach approximately $31 trillion—consistent with one-fifth of the anticipated federal financial obligation in 2044, relating to a rate of around $1.5 million per Bitcoin—an appraisal that shows a substantial boost from previous peak rates.
This outlook is not incapable of awareness; Bitcoin has actually shown comparable remarkable assessments throughout periods of significant gratitude. Moreover, as the United States federal financial obligation trajectory appears conservative, it is possible to prepare for Bitcoin obtaining approval as a traditional possession by 2044. By then, a bulk of the United States population will have engaged with Bitcoin throughout their adult lives, and a robust variety of financial items connected to Bitcoin is most likely to have actually emerged. In this context, inflation rates might intensify to 50% yearly, placing the United States federal government in alarming situations by 2044. A quick devaluation of the dollar would cause a speedy decrease in Treasury bond need, leaving decision-makers with couple of practical alternatives.
As such, possible actions of the United States federal government warrant assessment, particularly in relation to Bitcoin. Three circumstances will be thought about: the limiting action, including coercive steps versus Bitcoin’s competitors with the dollar; the palsied action, identified by governmental paralysis in the middle of Bitcoin’s ascendance; and the munificent action, in which Bitcoin is incorporated into the financial structure along with the United States dollar, assisting in financial stability.
Figure 3. Three United States financial circumstances
1. The Restrictive Scenario
Historically, federal governments dealing with currency decline usually turn to coercive methods to oblige residents to make use of the domestic currency, a practice called financial repression. In addition, they might enforce numerous financial limitations, consisting of rate controls and confiscatory tax, to sustain unwanted financial and financial policies. It is possible that the United States might embrace comparable methods as crises unfold.
Price Controls
In ADVERTISEMENT 301, the Roman Emperor Diocletian attended to inflation originating from the extended devaluation of the denarius by providing his Edictum de Pretiis Rerum Venalium, setting rate ceilings on over 1,200 items and services, consisting of earnings and important products. Diocletian associated increasing rates not to federal government excesses however rather to the expected greed of people.
Historical echoes of such actions resonate through time, with examples consisting of President Richard Nixon’s 1971 executive order that unilaterally decoupled the dollar from gold and implemented an across the country freeze on rates and earnings. Nixon likewise blamed “international money speculators” for the circumstance dealing with the American dollar.
Despite engaging proof showing the ineffectiveness of rate controls in reducing inflation, they stay politically appealing due to prevalent public understanding of instant security from increasing expenses. Since 2008, the Federal Reserve has actually participated in significantly aggressive steps to control what financial historians refer to as “the most important price”—the expense of obtaining cash as suggested by rate of interest. The Fed now puts in considerable impact over these rates through its primary trading of Treasury securities.
Capital Controls
Beyond rate controls, federal governments might also use capital controls to limit the conversion of regional currency into foreign possessions. Such steps have a historic precedent; throughout the Great Depression, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt released an executive order forbiding Americans from holding gold, persuading them into surrendering their gold holdings to the federal government in exchange for a repaired rate.
Modern examples of capital control appear in nations such as Argentina, which restricts residents from exchanging more than a small quantity of its currency for United States dollars, seemingly to support its currency. China likewise keeps rigorous capital controls, needing governmental approval for foreign currency exchanges to alleviate capital flight.
Growing approval amongst mainstream economic experts highlights modern capital controls as practical policy instruments for alleviating macroeconomic threats, which is a significant shift from earlier opposition driven by United States interests in keeping the dollar’s supremacy.
Under the 2044 limiting situation, the United States might release capital controls to block residents from transforming dollars into Bitcoin. Potential steps might consist of:
- Imposing a small suspension of dollar-to-Bitcoin exchanges, persuading the conversion of Bitcoin possessions into dollars at an established rate, no matter real market conditions.
- Prohibiting services in the United States from keeping Bitcoin reserves or accepting it as payment.
- Dissolving Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) by mandating their conversion to United States dollars at a repaired currency exchange rate.
- Forcing Bitcoin custodians to liquidate their possessions to the federal government at a set rate.
- Mandating people holding Bitcoin to offer it to the federal government at an established currency exchange rate.
- Introducing a reserve bank digital currency to diligently keep track of all dollar deals and prevent any purchases including Bitcoin.
Although total enforcement of these methods might show difficult, especially relating to self-custodied Bitcoin, compliance from a significant variety of obedient residents stays a possibility. Such steps are most likely to speed up more disintegration of self-confidence in the United States dollar, possibly costing the federal government upwards of $10 trillion in acquiring domestic Bitcoin holdings. Nonetheless, the federal government might see such alternatives as an essential option.
Confiscatory Taxation
Tax policies might also work as a system for the United States federal government to cut the usage and adoption of Bitcoin.
With Bitcoin forecasted to reach rates around $1.5 million per coin by 2044, a substantial part of the wealth created would be focused amongst early adopters and innovation business owners. This concentration of wealth might draw the ire of those without Bitcoin holdings, causing require limiting financial policies supporting the understanding of equity amongst residents.
Historical precedence exists for high boosts in capital gains taxes, consisting of conversations surrounding an 80% tax on cryptocurrency capital gains. Furthermore, propositions to tax latent capital gains—revenues not yet manifested through sales—have actually gotten traction in political discourse, regardless of considerable constitutional objections.
The application of such a tax would challenge legal meanings of earnings, triggering arguments about the tax of latent gains under the structure offered by the United States Constitution.
Additionally, distinct elements of United States tax policy need residents living abroad to pay taxes on both United States and regional earnings, incentivizing migrants to relinquish their citizenship. In a limiting situation, it is imaginable that the federal government might suspend the ability of Americans to renounce their citizenship, consequently making sure constant tax no matter residency.
Right-Wing Financial Restrictions
While lots of limiting steps might emerge from Democratic Party supporters, agents from the Republican Party might simply as easily harness populist discontent versus Bitcoin. The increase of an ideological motion called nationwide conservatism in the United States enhances a narrative encouraging of specific rights suppression supposedly for nationwide interests, highlighting financial and tax policies meant to strengthen the dollar versus viewed hazards from Bitcoin.
Examples of bipartisan propensities towards limiting steps can be seen following the September 11 attacks, when the U.S.A. PATRIOT Act was enacted to strengthen nationwide security at the cost of civil liberties, including rigid reporting procedures for foreign savings account and boosting anti-money laundering laws. Such legal tools might be repurposed to execute steps meant to cut the usage and ownership of Bitcoin.
The End of America’s Exorbitant Privilege
Bitcoin’s style shows impressive durability, keeping performance in spite of governmental limitations versus its usage. Notably, a substantial part of Bitcoin trading takes place in jurisdictions hostile to cryptocurrency, assisted in by technological methods such as virtual personal networks to mask user areas.
Assuming a theoretical situation in which a primary share of Bitcoin is owned by Americans, a significant part of which is protected versus seizure through self-custody, it is possible that any limiting steps would drive trading activity to decentralized platforms or jurisdictions with more beneficial guidelines.
A US financial crisis in 2044 would concomitantly lessen United States military abilities, which counts on comprehensive deficit-funded defense spending plans. This double crisis would compromise the federal government’s impact, possibly permitting smaller sized nations to end up being appealing options for Bitcoin financial investments previously held within United States borders. The emigration of Bitcoin wealth would even more worsen the financial difficulties dealing with the United States federal government.
Moreover, the weakening of Bitcoin’s energy within the US would stop working to persuade foreign financiers relating to the practicality of United States Treasuries, engaging the federal government to raise rate of interest drastically to bring back appeal. This would, in turn, pump up loaning expenses, consequently worsening financial concerns.
Eventually, it might end up being a requirement for the United States to denominate its bonds in Bitcoin or a currency pegged to Bitcoin to protect foreign financial investments. Such a huge shift would signify the decrease of the “exorbitant privilege” traditionally managed to the United States—the capability to obtain in its own currency, allowing the devaluation of financial obligation worth. Under a Bitcoin requirement, dollar decline might increase commitments towards financial institutions, placing financial institutions to require austerity steps to remedy financial disparities.
A substantial decrease in military financing would yield extensive geopolitical implications, raising issues relating to the stability of power characteristics in between excellent countries. Historical precedence recommends that such shifts typically accompany increased international stress.
2. The Palsied Scenario
The term “palsy” describes paralysis accompanied by uncontrolled motion—a fitting description of the 2nd situation identified by the unpredictable financial environment arising from Bitcoin’s increase while concurrently coming to grips with governmental paralysis and political department within the United States. Under this situation, the United States discovers itself incapable of taking definitive action versus Bitcoin while stopping working to remedy its financial difficulties.
The present political environment in the United States shows an unmatched level of partisan department, with the electorate significantly arranged by cultural qualities. Recognizable patterns recommend that lots of Independents deal with difficulties in taking part meaningfully in elections controlled by the options of celebration bases.
While the hope stays for these patterns to reverse, numerous elements might add to their entrenchment. The quick development of innovation efficient in mass behavioral adjustment, consisting of expert system, provides threats that might piece rely on social and political organizations, making complex consensus-building efforts on prominent concerns such as privilege reform.
In this palsied situation, the United States federal government would have a hard time to enact the limiting steps defined formerly. Political department might prevent Congress and the Federal Reserve from developing digital currencies or enforcing confiscatory tax on Bitcoin holders due to pushback from the public and prominent banking sectors that concern such relocations as existential hazards.
However, it is necessary to keep in mind that this situation will not symbolize a libertarian paradise. The federal government maintains authority over the guideline of central exchanges and associated financial services, possibly restricting the volume of capital negotiated in Bitcoin.
Consequently, while bitcoin-holding Americans might come across less barriers to possession security compared to the limiting situation, the institutional structure within which they run would stay mainly paralyzed. Accordingly, the clash in between policymakers resistant to Bitcoin and political factors encouraging of the cryptocurrency might result in stalemate.
Yet, must the Treasury bond market face devastating failure, an alarming financial environment may move the United States to urgently straighten its financial structure. Should this happen, it is imaginable that Treasury-associated entities will look for to utilize Bitcoin as a supporting possession, boosting the potential customers for renewing the United States financial structure.
3. The Munificent Scenario
The munificent situation provides an engaging yet positive vision for the United States in 2044, identified by proactive policymaking that looks for to remain ahead of impending crises instead of simply respond to external pressures.
In this story, the United States might replicate the current actions of nations such as El Salvador and Argentina, whose leaders welcomed Bitcoin in action to financial turbulence. An election in November 2044 might give power a pro-Bitcoin president efficient in presenting Bitcoin as legal tender along with the dollar. Anticipating shared concessions in between Treasury shareholders and the federal government, ideas of partial financial obligation defaults, Medicare, and Social Security reform might emerge, eventually paving the method for a sound dollar-backed by Bitcoin.
Such possible reforms require not downside susceptible populations. Research recommends that financial solvency can line up with social well-being policies. Proposed legislation, such as the Fair Care Act of 2020 and reforms to Social Security that pivot the trust fund’s possessions towards Bitcoin-denominated securities, might secure the senior and financially disadvantaged while cultivating total financial stability.
Realigning the United States financial structure with Bitcoin concepts might develop the structure for a renaissance of American success, distanced from adversarial financial paradigms. The mix of United States entrepreneurial culture and financial stability positions the country for a date of unmatched financial development, contingent upon the prioritization of long-lasting interests over instant political gain.
The Satoshi Papers is now offered for pre-order in the Bitcoin Magazine Store.
Thank you for visiting our site. You can get the latest Information and Editorials on our site regarding bitcoins.